Answer
Nov 10, 2025 - 09:58 AM
The main difference between the two types of isolators is the amount of voltage drop (power loss) they create. "Standard Isolators" typically refers to Diode-Based Isolators, while FET Isolators (Field-Effect Transistor) use advanced solid-state technology to virtually eliminate this power loss.
Comparison: FET Isolator vs. Diode Isolator
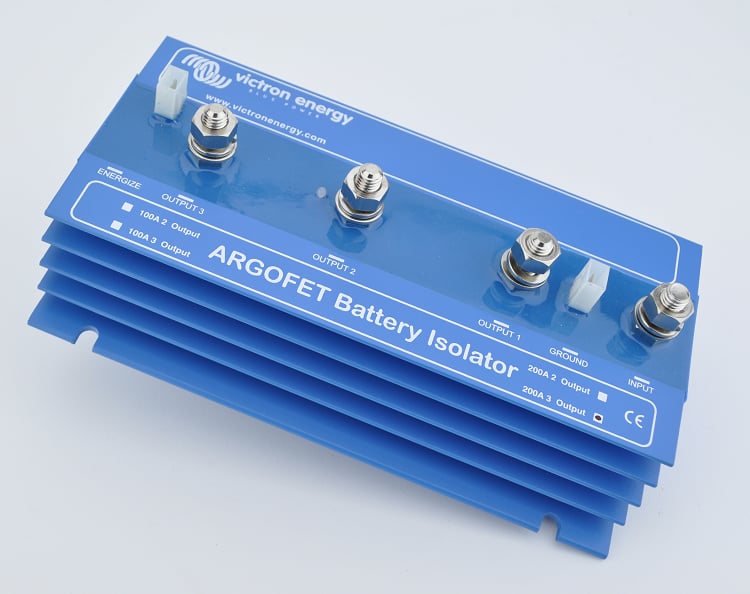
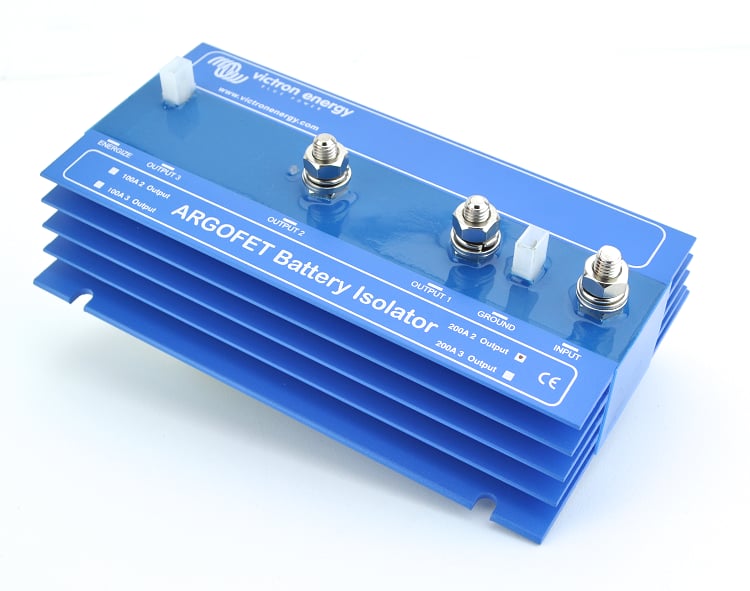
At PKYS we sell four versions of the Victron ArgoFets. These FET Isolator models vary in the number of outputs and the maximum current rating. In summary: While a standard diode isolator is a simple and cheaper solution to isolate battery banks, a modern FET isolator is significantly more efficient because it prevents the critical voltage drop that hinders proper battery charging
Comparison: FET Isolator vs. Diode Isolator
| Feature | FET (Field-Effect Transistor) Isolator | Standard (Diode-Based) Isolator |
| Technology | Advanced solid-state semiconductor switches (FETs). | Simple semiconductor diodes. |
| Voltage Drop | Virtually None (typically < 0.2 Volt at high current). | Significant (typically 0.6 to 1.0 Volt). |
| Charging Efficiency | High. Batteries receive almost the full alternator voltage, leading to faster, more complete charging. | Lower. The voltage drop can prevent batteries from reaching a 100% state of charge. |
| Heat Generation | Minimal, though cooling fins may still be used for high-amperage units. | Generates more heat due to power loss across the diodes. |
| Cost | Generally Higher. | Generally Lower. |
| Alternator Adjustment | Usually not required. | Often required to increase the alternator's output voltage to compensate for the drop. |